How Will You Charge Your EV Fleet?
Transportation is going electric, and organizations should start to familiarize themselves with the knowledge and tools needed to successfully navigate EV charging and infrastructure for their futu…
Strategize your EV implementation approach.
Measure: The first step is to quantify your fleet’s current performance through fleet data analysis. After conducting a comprehensive review of vehicle usage, driver behavior, and other information, your organization can confidently project cost savings.
Model: Next, you’ll want to create a strategic EV implementation model for your organization. This will include vehicle size and range recommendations, charging and fueling needs, sustainability and savings.
Adopt: The final step is to set a timeline to execute the full EV adoption process. In addition to installing the necessary EV infrastructure, stakeholders must also include a plan for employee training and driver implementation.
Merchants Fleet has a team of fleet electrification experts ready to help you bridge the gap between strategy and execution. Their knowledge in vehicles, charging infrastructure, financial incentives, and more can help you become an industry leader and embrace the EV adoption journey.
Electric vehicles are loaded with the latest and greatest in technology, but they also require an upfront investment of the right chargers to keep them moving. Our Fleet Electrification Team has the infrastructure experience needed to scope out plan for your installation needs.
The automotive industry is heading towards an electrified future, during this transition we understand that EVs won’t be right for every application. The best way to learn this is through a pilot test. Merchants has programs in place to help fleets get the right vehicles if their first EVs don’t meet their needs.
Transportation is going electric, and organizations should start to familiarize themselves with the knowledge and tools needed to successfully navigate EV charging and infrastructure for their futu…
There are 5 steps to EV Adoption: Learn, Align, Plan, Pilot, and Adopt. This panel discussion will dive into the Align and Plan phases of adoption. What is important to know, what trends are emergi…
Less moving parts means less maintenance downtime. Plus, EV telematics and data reveal game-changing business insights that can maximize efficiency for long-term cost savings.
EVs are regarded as one of the fastest ways to achieve a positive sustainability impact, while also driving the bottom line.
Eliminating tailpipe emissions in your fleet by switching to EVs is an incredible way your organization can reduce its carbon footprint.
EV models generally have the most modern driver assistance tech available, helping increase driver safety.
EVs come in a variety of makes and models, and more are continuing to be developed. Our EV finder tool makes it easy for you to search by vehicle specs, battery capacity, range, and more.
AEVs/BEVs run entirely on an electric motor powered by a large internal battery. They must be plugged in to charge and use regenerative braking to reduce wasted energy while driving.
PHEVs have both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. They can charge their batteries through regenerative braking, like a HEV, but have a larger battery and can be plugged in to be charged. Some PHEVs can be propelled by their battery for short distances, thus reducing gasoline consumption. They can be refueled with gasoline like an internal combustion engine vehicle.
HEVs are powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric motor that uses a smaller internal battery compared to a BEV. A traditional hybrid is recharged through regenerative braking and receives most of its energy through gasoline.
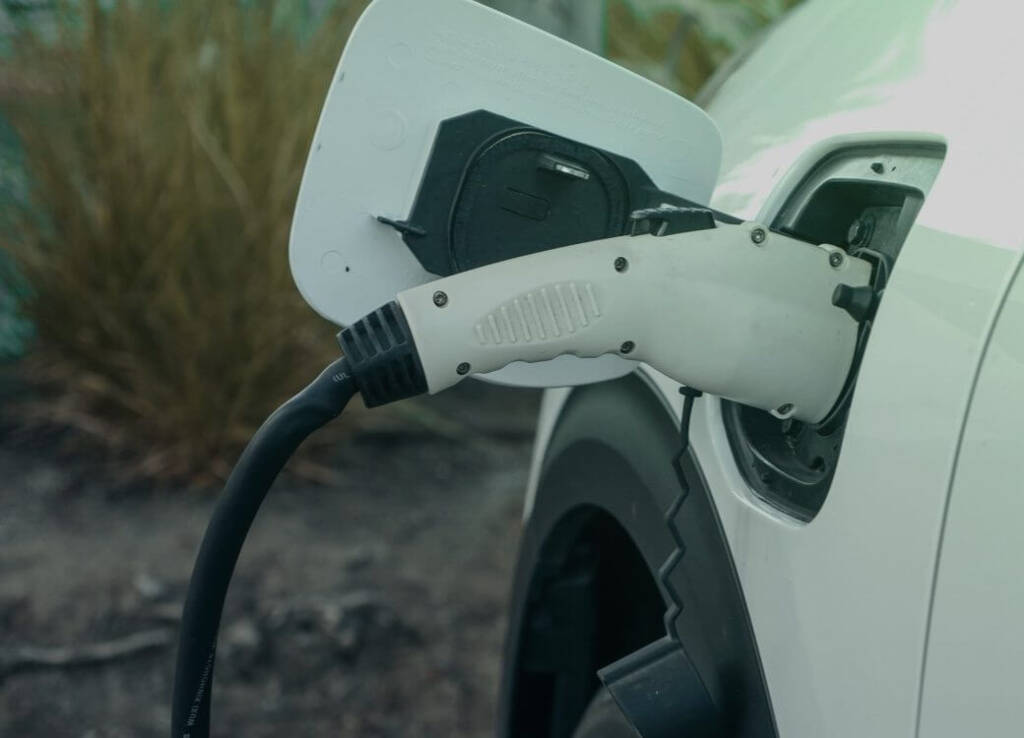


There are two primary factors that determine how fast an electric vehicle charges; the amount of power that the charging station can dispense, and the amount of energy a particular EV can accept. As for the supply, there are three “levels” of charging.

This is essentially plugging into a standard household wall outlet. Level 1 charging presents the slowest charging speed as it provides around 1 kW of power.

These are commonly found in parking lots, at businesses, and in homes. This is the type of charger you would likely install at your garage/facility for recharging a fleet.

These are the ultra-fast chargers that you’ll find on the side of highways and in highly populated electric car areas. These are beginning to proliferate across the U.S.
Merchants has the right technology, skilled expertise, and experience to assess your fleet needs and identify the roadmap for your organization’s EV adoption.
